Understanding Ghrelin: Your Body's Hunger Messenger
Ever wonder why your stomach rumbles or why you feel hungry even after eating? A hormone called ghrelin is at work. Ghrelin signals your brain when it's time to eat, making it an important player in controlling your hunger and maintaining energy balance. Let’s break down what ghrelin does and why it’s important for your health.
What Is Ghrelin and How Does It Work?
Ghrelin is often called the "hunger hormone" because it triggers appetite. It’s mainly made in your stomach and released into your blood when your stomach is empty. When ghrelin levels rise, your brain gets a signal to make you feel hungry. After you eat, ghrelin levels drop, so you feel full. It helps your body know when to eat and when to stop.
Besides controlling hunger, ghrelin also affects how your body uses energy. It can slow down your metabolism to save energy when you haven’t eaten for a while. This function helped humans survive during times without food but can make weight management tricky today.
Why Ghrelin Matters for Weight and Metabolism
If you’re trying to lose weight, ghrelin can be a double-edged sword. Dieting and fasting often cause ghrelin levels to increase, making you feel hungrier and encouraging you to eat more. That’s why many people struggle with hunger pangs during weight loss.
Understanding ghrelin’s role means you can better plan your meals and snacks to keep hunger under control. For example, eating protein-rich foods, fiber, and healthy fats can help keep ghrelin levels steadier. Also, getting enough sleep is key—poor sleep raises ghrelin levels and makes you feel hungrier the next day.
Researchers are also looking into how ghrelin relates to conditions like obesity, eating disorders, and even diabetes. While it’s not the only hormone involved in hunger and metabolism, ghrelin plays a big part in how your body balances energy intake and usage.
Next time you feel hungry, remember ghrelin is likely behind the scenes, nudging you to eat. By learning to work with this hormone, you can make smarter choices about eating and managing your health.
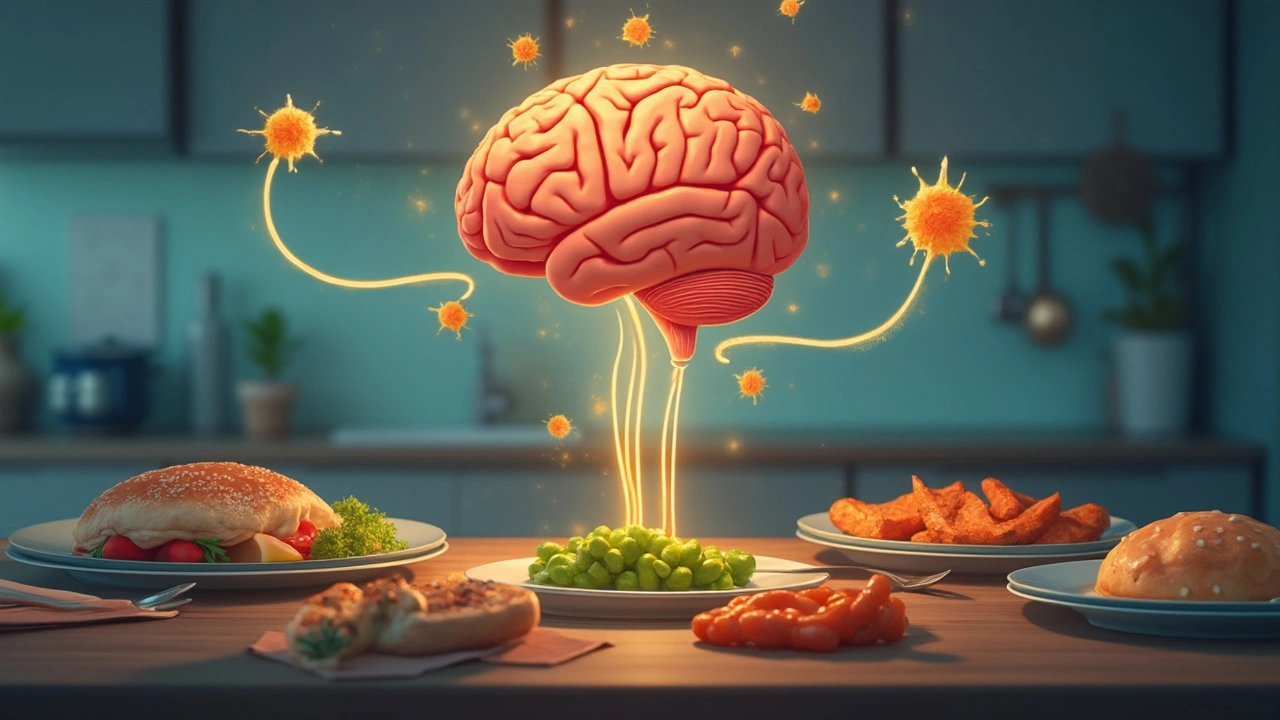

Serotonin, SSRIs, and Appetite: How Brain Chemistry Impacts Hunger
This article unpacks the science behind how SSRIs—commonly prescribed antidepressants—affect your appetite by influencing key hormones like ghrelin and leptin. It explores the close link between serotonin levels in the brain and feelings of hunger or fullness, giving a practical look at why some people notice weight or appetite changes on SSRIs. Learn what researchers really know, what to expect, and simple tips for managing satiety while taking these medications.
View More