Formoterol – Long‑Acting Bronchodilator Overview
When working with Formoterol, a long‑acting β2‑agonist inhaled medication that keeps airways open in asthma and COPD. Also known as Foradil, it delivers steady bronchodilation over 12 hours, making it a cornerstone of maintenance therapy. Bronchodilator, a drug class that relaxes airway smooth muscle to improve airflow is the broader category that Formoterol belongs to. In the context of Asthma, a chronic inflammatory disease of the airways causing wheeze and shortness of breath, Formoterol works alongside a quick‑relief inhaler to control symptoms day‑to‑day. The drug’s long‑acting nature means patients can reduce the frequency of rescue inhaler use, which in turn can lower overall steroid exposure.
The typical dosage comes as a metered‑dose inhaler (pMDI) or a dry‑powder inhaler (DPI), delivering 12 µg or 6 µg per puff depending on the brand. The recommended maintenance dose is usually two puffs twice daily, but doctors adjust it based on lung function tests and symptom patterns. Because Formoterol is a Formoterol that activates β2‑adrenergic receptors, it starts working within minutes and lasts up to 12 hours, blending the fast action of a rescue inhaler with the sustained effect of a maintenance drug. Patients should be aware of common side effects such as tremor, throat irritation, or mild palpitations; serious risks include paradoxical bronchospasm or heart rhythm changes, especially when combined with certain other stimulants.
Practical Tips and Related Resources
Choosing the right inhaler device matters. DPIs require a strong, fast inhalation, while pMDIs need coordinated breathing with actuation. Many patients find a spacer helpful with pMDIs to reduce oral deposition and improve drug delivery. When starting Formoterol, doctors often prescribe a short‑acting β2‑agonist like albuterol as a rescue option, ensuring rapid relief if symptoms flare unexpectedly. Monitoring tools such as peak‑flow meters or spirometry can track how well Formoterol is controlling airflow, allowing adjustments before an exacerbation occurs.
Beyond the medication itself, lifestyle factors play a big role. Reducing exposure to allergens, quitting smoking, and staying active support the drug’s effectiveness. For those managing COPD, Formoterol is often paired with a long‑acting antimuscarinic agent (LAMA) to address both bronchoconstriction pathways. This combination strategy aligns with current guidelines that promote dual bronchodilation for better lung function and quality of life.
Below you’ll find a curated set of articles that dive deeper into buying affordable generic medications, comparing inhaler options, and handling chronic respiratory conditions safely. Whether you’re looking for price‑saving tips, side‑effect management, or broader disease‑management advice, the collection offers actionable insights to help you get the most out of Formoterol and related treatments.
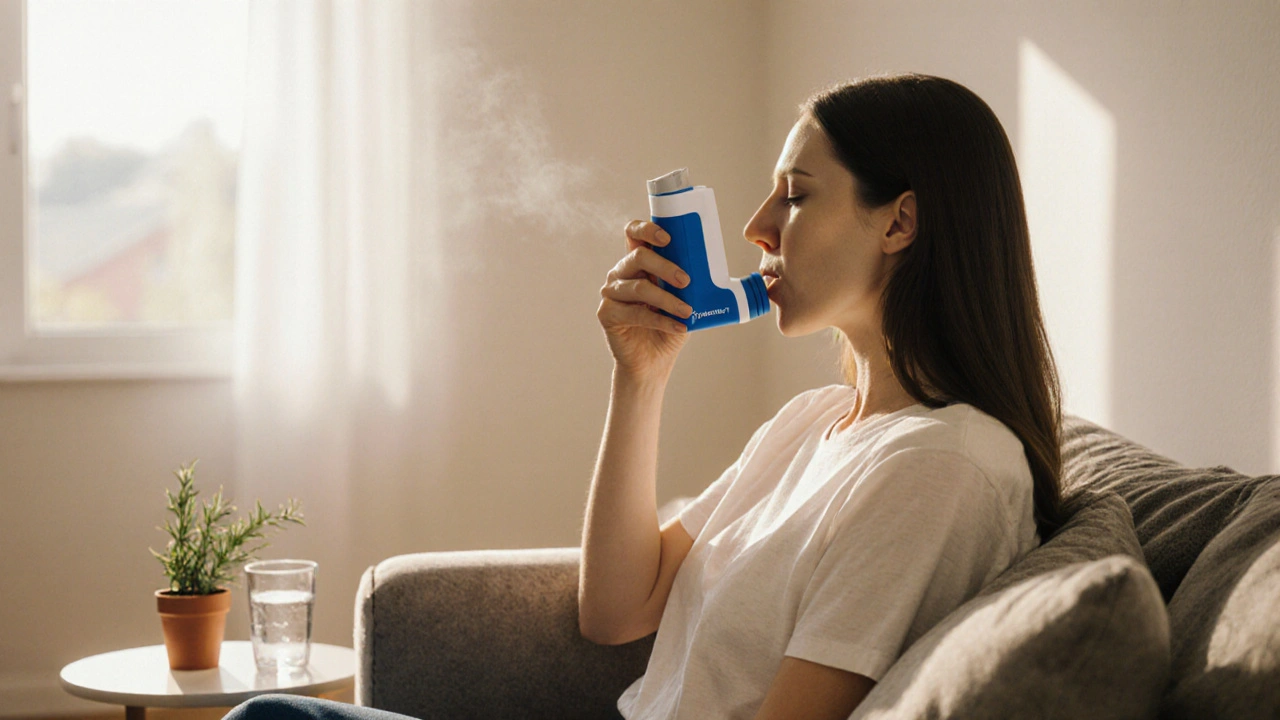

Symbicort (Budesonide/Formoterol) vs. Top Alternatives: Which Inhaler Fits Your Needs?
Compare Symbicort with leading inhaler alternatives, weigh efficacy, safety, cost and device ease to find the best fit for asthma or COPD management.
View More